The Dual-Switch Architecture of UPI: Why Your PSP's Tech Matters More Than You Think
The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has transformed digital payments in India, becoming the preferred mode for billions of transactions every month. Behind the simplicity of tapping a button lies one of the most sophisticated payment infrastructures in the world. For enterprises, fintechs, and Payment Service Providers (PSPs), the technology decisions made at the backend can mean the difference between seamless payments and frustrated users. At the heart of this conversation is the UPI Switch architecture — particularly the dual-switch setup that underpins reliability and scalability.
In this blog, we’ll demystify how UPI’s switching layer works, why PSP-level switching matters, and what enterprise CTOs and startup tech leads should consider when designing or partnering for payment infrastructure in India.
What is a UPI Switch?
AU PI switch is the routing engine that connects banks, PSPs, and the NPCI (National Payments Corporation of India) network. It ensures that every “pay” or “collect” request finds its correct destination, manages retries, and balances traffic during peak load.
For PSPs, the switch isn’t just a compliance requirement — it’s a performance differentiator. The UPI PSP switch directly influences transaction success rates, latency, and resilience. In high-volume markets like India, where transaction surges during festivals or sales are common, switch efficiency determines customer trust.
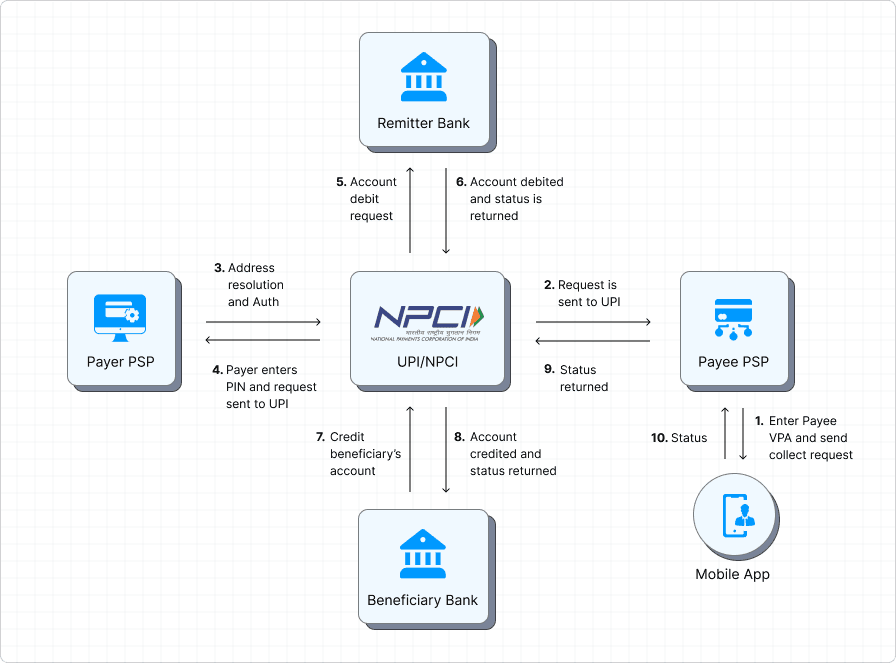
Why a Dual-Switch Architecture Matters
The traditional single-switch setup can quickly become a bottleneck under high load. The dual-switch architecture — a design where two switching layers run in tandem — addresses this challenge by:
Load balancing: Requests are distributed across two switches, reducing the risk of congestion.
Failover reliability: If one switch fails, the second ensures continuity.
Geographical redundancy: Dual switches placed in different regions reduce latency and provide resilience against regional outages.
In practice, this means that when a festival sale triggers millions of transactions in minutes, users experience smooth payments because the load is intelligently managed.
The Building Blocks of Dual-Switch UPI Architecture
The UPI switch architecture relies on several technical components:
Routing engine: Decides the path of each transaction request.
Transaction queue management: Ensures retries and backoffs are handled without overwhelming systems.
Security layers: Encryption (in transit and at rest) and compliance with NPCI mandates.
Monitoring and observability: Real-time dashboards for PSPs to track success rates, latency, and bottlenecks.
API gateways: Interfaces that let third-party apps and merchants access switching capabilities.
The UPI PSP switch is thus both a compliance gateway and a performance-critical component of the overall payment infrastructure in India.
How PSPs Benefit from Dual-Switch Setups
For PSPs, dual-switch setups aren’t just about uptime; they bring tangible advantages:
-
Higher transaction success rates: Distributing traffic reduces failed attempts.
-
Optimized costs: Intelligent routing minimizes retries, saving bandwidth and processing costs.
-
Scalability: Enterprises can handle growth without major architectural overhauls.
-
Regulatory alignment: With the August 2025 NPCI updates emphasizing UPI switch architecture standards, dual-switch models are increasingly seen as best practice.
This directly impacts both enterprise-scale players and startups. While large PSPs use dual switches for resilience, nimble fintech startups adopt them early to compete with bigger incumbents.
Challenges in Implementing a Dual-Switch
Adopting a dual-switch is not without challenges:
Integration complexity: Syncing two switches requires consistent state management.
Latency concerns: Without proper routing logic, dual switches can add overhead instead of reducing it.
Cost of redundancy: Maintaining two parallel infrastructures increases operational expenditure.
Yet, when designed well, these challenges are outweighed by long-term benefits. PSPs that treat their UPI PSP switch as a strategic asset rather than a compliance checkbox will see higher reliability and customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for CTOs and Tech Leads
Here’s how technology leaders can approach the dual-switch design:
Plan for scale from day one: Assume transaction volumes will double annually, and design the UPI switch architecture accordingly.
Use intelligent routing: Employ health checks and real-time load metrics to distribute traffic effectively.
Automate failover: Manual interventions defeat the purpose of redundancy. Automation ensures zero downtime.
Leverage observability tools: Invest in APM (Application Performance Monitoring) systems that track switch-level metrics.
Whether using in-house switches or third-party providers like IndiNXT, align on SLAs, compliance, and latency expectations.
Where IndiNXT Comes In
For PSPs and fintechs, building a dual-switch setup from scratch can be resource-intensive IndiNXT offers a modular switching layer that is UPI-ready, API-first, and designed for high availability. With intelligent routing and compliance-first design, IndiNXT helps PSPs focus on customer experience while ensuring their UPI PSP switch meets performance and regulatory benchmarks.
By acting as a routing and optimization layer, IndiNXT reduces failed attempts, improves transaction throughput, and ensures resilience — critical for enterprises competing in India’s high-volume digital payments space.
Final Thoughts
The dual-switch architecture of UPI is more than just a redundancy measure — it’s the foundation of reliability in India’s payment ecosystem. As transaction volumes soar and payment infrastructure in India matures, PSPs that invest in resilient, intelligent switching will stand out.
For enterprise CTOs and startup tech leads, the message is clear: your switch isn’t just backend plumbing. It’s the backbone of your customer experience and your competitive edge. By embracing dual-switch setups and leveraging partners like IndiNXT, PSPs can future-proof their infrastructure and deliver payments that are fast, reliable, and trusted.
It’s a setup where two UPI switches operate in parallel to ensure load balancing, failover reliability, and geographical redundancy.
The UPI PSP switch directly impacts transaction success rates, latency, and scalability. A robust switch design translates to smoother user experiences.
While not mandatory yet, the August 2025 updates strongly recommend dual-switch adoption as part of evolving UPI switch architecture standards.
Poor routing logic, lack of synchronization, and underinvestment in monitoring tools can make dual switches less effective.
IndiNXT offers modular infrastructure that integrates seamlessly with PSP systems, providing intelligent routing, observability, and compliance support.






